 EM: Databases/SQL: Databases
> Settings
EM: Databases/SQL: Databases
> Settings
Description
The  Databases, Settings provides a centralized location for managing general database properties, allowing administrators to configure categorized options controlling data handling, access behavior, character rules, table creation behavior, miscellaneous settings, and custom functionality that define database operation within Enterprise Manager.
Databases, Settings provides a centralized location for managing general database properties, allowing administrators to configure categorized options controlling data handling, access behavior, character rules, table creation behavior, miscellaneous settings, and custom functionality that define database operation within Enterprise Manager.
Note: selecting a database from  Databases name list, opens its configuration interface, enabling access to Settings and other databases.
Databases name list, opens its configuration interface, enabling access to Settings and other databases.
Location
![]() EM Navigator →
EM Navigator →  Databases/SQL →
Databases/SQL →  Databases → Settings
Databases → Settings
Toolbar
| Button | Function |
|---|---|

|
Adds new user property. |
|
Refreshes the Directory Name field. |
|
|
Deletes a selected directory. |
|

|
Allows the selection of file(s) from the local system. |

|
Allows to create new file/folder. |
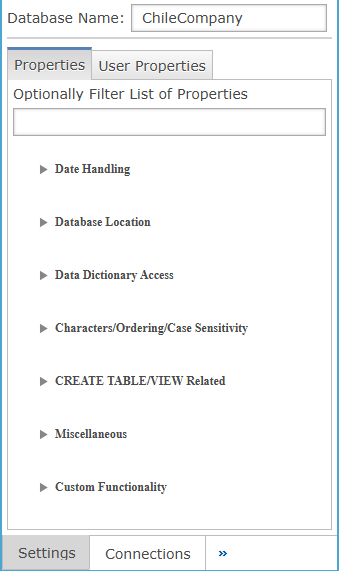
Database Properties Header Panel
This panel shows which database is currently selected and serves as the entry point for accessing and managing its available configuration sections and related settings.
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Database Name | The name of the currently selected database being configured. |
| Properties | Opens the main database configuration panel displaying categorized system properties for the selected database. |
| User Properties | When selected it opens the User Properties workspace, where administrators manage database specific custom properties, and clicking  to launch the Add User Property dialog for defining, categorizing, and configuring new metadata fields. to launch the Add User Property dialog for defining, categorizing, and configuring new metadata fields. |
| Optionally Filter List of Properties | Filters visible database properties by entered text, helping users quickly locate specific configuration entries. |
Add User Property
The User Props sub-tab allows the user to define properties and values
for those properties. Access these properties from SQL statements using
the GLOBAL scalar function (see SQL
- Custom Functions). These properties can also specify additional
directories that data files can be found in (i.e. DATA1, DATA_NM, etc.). The Add User Property pane opens after clicking the  button in the User Properties pane, allowing administrators to define custom database properties with names, categories, data types, validation rules, and selection behavior.
button in the User Properties pane, allowing administrators to define custom database properties with names, categories, data types, validation rules, and selection behavior.
Add User Property Settings
| Settings | Description | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category |
The user property to a grouping that organizes properties within database settings.
|
||||||||||||||||
| Property Name | The unique identifier for the custom property used internally to reference and store values. | ||||||||||||||||
| Display Name | The name for the property. | ||||||||||||||||
| Description | The explanatory text describing the property’s purpose, usage context, and behavior for administrative reference. | ||||||||||||||||
| Type |
The data type used to store and validate the custom property value.
|
||||||||||||||||
| Valid Values | Clicking the  icon opens the Valid Values window, then click the icon opens the Valid Values window, then click the  icon to create a new entry, which appears as New Value 0, by clicking the type, in dropdown, any displayed data can be selected, then editing the Display Name and Value fields user can define custom naming and values credentials. As last step, clicking OK to save and populate the Valid Values field. icon to create a new entry, which appears as New Value 0, by clicking the type, in dropdown, any displayed data can be selected, then editing the Display Name and Value fields user can define custom naming and values credentials. As last step, clicking OK to save and populate the Valid Values field. |
||||||||||||||||
| Max Value Count | The maximum number of values allowed to be assigned to this property. | ||||||||||||||||
| Chooser Type |
The selection interface used when users choose values for this property.
|
Date Handling
Since BBj string templates do not have a date type field, BBj uses date suffixes to determine if a field should be treated as a date value. Use this section to specify one or more date suffixes and the format that should be used to evaluate the date data. Specify multiple date suffixes by separating each suffix with a comma. If multiple date formats are used within a single database (not advisable), up to three different formats can be specified.
Date Handling Settings
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Date Format |
Conversion class to use to convert the raw data in the column to a usable date. The list displayed in the combo box is a list of all date formats available on this BASIS DBMS (including custom date formats). |
| Date Column Suffix | Column suffix to use to determine if a column should be treated as a DATE type. This means that any column whose name ends with the date suffix will be considered a DATE type and apply the specified date format before evaluation. |
| Y2K Window | Used by date formats that store dates as 2 digit years. These date formats add 1900 to those that are greater than the Y2K window value, and add 2000 to those less than the value. |
Database Location
The Database Location section specifies the database’s DATA and DICTIONARY file locations, linking the database definition to the correct paths used for accessing tables and data dictionary files.
Database Location Settings
Data Dictionary Access
The Data Dictionary Access section defines which user credentials are used to access data dictionary files, supporting service, connected, or specific users for controlled database dictionary operations.
Characters/Ordering/Case Sensitivity
The Characters/Ordering/Case Sensitivity section configures encoding, sorting behavior, case handling, and collation options, controlling how text values are interpreted, indexed, compared, and ordered during SQL processing and query execution.
Characters/Ordering/Case Sensitivity Settings
| Settings | Description | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encoding Character Set | Character set to use for encoding/decoding values in the database. The dropdown provides supported BASIS and standard encodings such as Big5, CESU-8, EUC-JP, and x-BASIS variants. | ||||||
| Ordering Type |
Keys on non-ESQL BBj data files order character values based on byte (ASCII) value instead of “collation” order based on the alphabetizing rules of the English language. Because of this, lower case letters sort after all capital letters. This option allows user to specify the way ordering should be handled by ORDER BY. With collation order enabled, ORDER BY sorts values according to alphabetizing rules. With byte order enabled, it sorts according to ASCII character values. With collation order enabled, the SQL engine cannot rely on the key order for optimization purposes on sorting operations. However, this may not impact any of your queries since the SQL engine can still optimize on WHERE clauses and always chooses WHERE clause optimization over ORDER BY optimization when it has a choice between to the two.
|
||||||
| Case Insensitive Keys |
|
||||||
| ESQL Collation |
|
CREATE TABLE/VIEW Related
The CREATE TABLE/VIEW Related section defines default table types, key enforcement, date handling, and view capabilities, controlling how new database objects are created and structured.
CREATE TABLE/VIEW Related Settings
| Settings | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREATE TABLE Type |
Specifies the default type of data file to create when executing a CREATE TABLE statement.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Full-Featured CREATE VIEW |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strict Key Checking |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default Date Type Definition |
If a type definition is selected here, CREATE TABLE statements will assign this type definition as the underlying data type for all DATE type columns.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default Date Format |
The date format to use when creating a table and specifying a DATE type column. Used in conjunction with Default Date Type Definition.
|
Miscellaneous
The Miscellaneous section contains additional database configuration options that affect runtime behavior, compatibility, and performance. Administrators should review each setting carefully, even if not currently required, to understand the full range of capabilities available for BBj database environments.
Miscellaneous Settings
| Settings | Description | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default Numeric Scale | The scale used for NUMERIC columns in Legacy and Barista format databases. These formats do not support a scale attribute on column definitions so BBj uses this default scale when returning column information to JDBC and ODBC API calls. | ||||||||||||||||
| SPROC Debugging |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Legacy Handle Variable Right-Padded |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Consistent Fixed Length Padding |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Pad Character | If the Consistent Fixed Length Padding setting is enabled, this is the pad character that will be used for padding | ||||||||||||||||
| Truncate If Too Long |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Auto Analyze Tables |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Equality Optimize NUMERICs |
|
||||||||||||||||
| NUMERIC Empty String as Zero |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Read Only |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Type | Read-only indication of the type of the database. | ||||||||||||||||
| Enforce VARCHAR Length |
|
||||||||||||||||
| SPROC Run As User |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Optimize Date Columns |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Advisory Locking |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Auto Commit |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Timeout(ms) | The number of ms to wait for file access operations to complete if necessary. If the timeout is reached before completing the file operations, an error will occur. | ||||||||||||||||
| Statement Timeout(sec) | Timeout in seconds for file access operations that occur inside SQL statements such as write, remove, and read. | ||||||||||||||||
| SPROC Classpath |
Select a specific configured classpath to use when executing stored procedures. If none is specified, stored procedures will execute using the default classpath for BBjServices.
|
Custom Functionality
The Custom Functionality section configures advanced SQL behavior, including factory implementations and optional scalar or group function classpaths, enabling database extensions through custom logic components.
Custom Functionality Settings
| Settings | Description | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBjSQLFactory Implementation | Specifies the SQL factory implementation used by the database to resolve and execute custom SQL functionality. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scalar/Group Function SSCP |
Selects the classpath source containing custom scalar or group SQL functions available to the database.
|