 EM: BBj Services > Servers
EM: BBj Services > Servers
Description
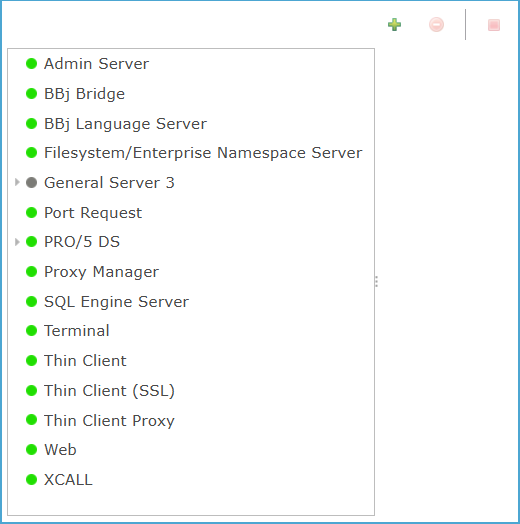
The  Servers panel in Enterprise Manager centralizes the management of all BBj server processes running within the system. Each entry in the list represents a specific server type that provides core functionality, including administration, SQL services, client connections, inter-process communication, web access, and legacy PRO/5 integration. Interaction with this panel allows administrators to configure server properties, monitor status, and control execution. The icons in the upper-right corner provide the ability to add a new server instance, remove the selected server, or pause active operations. The list of supported server types includes: Admin Server, BBj Bridge, BBj Language Server, Filesystem/Enterprise Namespace, Port Request, PRO/5 DS, PRO/5 DS, Memory Mapped Protocol, Proxy Manager, SQL Engine Server, Terminal, Thin Client, Thin Client (SSL), Thin Client Proxy, Web, and XCALL.
Servers panel in Enterprise Manager centralizes the management of all BBj server processes running within the system. Each entry in the list represents a specific server type that provides core functionality, including administration, SQL services, client connections, inter-process communication, web access, and legacy PRO/5 integration. Interaction with this panel allows administrators to configure server properties, monitor status, and control execution. The icons in the upper-right corner provide the ability to add a new server instance, remove the selected server, or pause active operations. The list of supported server types includes: Admin Server, BBj Bridge, BBj Language Server, Filesystem/Enterprise Namespace, Port Request, PRO/5 DS, PRO/5 DS, Memory Mapped Protocol, Proxy Manager, SQL Engine Server, Terminal, Thin Client, Thin Client (SSL), Thin Client Proxy, Web, and XCALL.
Location
![]() EM Navigator →
EM Navigator →  BBjServices →
BBjServices →  Servers
Servers
Toolbar
Admin Server
The Admin Server provides centralized control of BBjServices, handling startup, shutdown, and monitoring of server processes. Settings define interface, port, logging, retention, and debug levels, with options for backlog, blocking, and SSL security through keystore and password configuration. Enabling Start ensures the Admin Server launches automatically, making it essential for managing the environment.
Admin Server Settings List
BBj Bridge
BBj Bridge acts as a communication gateway between BBjServices and external systems or clients. It enables external applications to connect to BBj by listening on a specific network port.
BBj Bridge Settings List
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Start |
|
| Bind Address | Specifies the IP address the bridge will listen on (0.0.0.0 for all interfaces). |
| Port | Defines the network port used for incoming connections. |
| Maximum Clients | Limits the number of concurrent client connections allowed. |
| Allow Rhosts |
|
BBj Language Server
The BBj Language Server executes BBj programs and manages program runtime requests from clients, serving as the execution engine for BBj applications. Configuration options specify the hostname and communication port used for accepting connections, while the Start option controls automatic initialization when BBjServices launch. As a core runtime component, the BBj Language Server ensures that applications written in BBj can be compiled, interpreted, and run consistently within the managed service environment.
BBj Language Server Settings List
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Start |
|
| Hostname | Specifies the network name or IP address where the BBj Language Server binds and accepts client connections, with localhost as the default value restricting access to the local machine unless changed to a resolvable hostname or external IP address. |
| Port | Defines the TCP/IP port number on which the BBj Language Server listens for client connections, with the default value of 5008 unless reassigned to a different, non-conflicting port by the administrator. |
Filesystem/Enterprise Namespace Server
The Filesystem/Enterprise Namespace Server manages client access to directories, files, and enterprise namespace resources, acting as the service layer that maps logical file references to physical storage locations. Configuration settings define operational parameters such as port, log file details, debug and log levels, blocking mode, SSL encryption, and authentication handling through rhost and Ident verification. Additional options control root scanning and allow administrators to set path prefixes and DSKSYN mappings, ensuring secure and efficient access to file system resources within BBjServices.
Filesystem/Enterprise Namespace Server Settings List
| Settings | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start |
|
||||||||||||
| Interface | Defines the IP address or network interface on which the server listens for client requests. The default value 0.0.0.0 binds the service to all available network interfaces, allowing connections from any configured address. | ||||||||||||
| Port | Defines the TCP/IP port through which the server accepts client connections. The default value 2000 can be changed by the administrator to prevent conflicts with other services or to meet network security requirements. | ||||||||||||
| Log File Base | Specifies the file path and name where the server writes its log output. The default entry C:\bbx\log\FilesystemServer.log records operational events and can be redirected to a different location if required by administrative policy. | ||||||||||||
| Log File Size (MB) | Defines the maximum size, in megabytes, that an individual log file can reach before a new file is created. The default value 10 MB ensures logs remain manageable and prevents excessive disk usage. | ||||||||||||
| Keep Logs (Days) | Specifies the number of days server log files are retained before automatic deletion. The default value 7 days ensures recent activity is preserved while preventing excessive disk usage from old logs. | ||||||||||||
| Debug Level | Controls the amount of diagnostic detail recorded in the server log. Level 0 disables debug output, while Levels 1 through 4 progressively increase the depth of diagnostic information, with Level 4 providing the most comprehensive details for troubleshooting. | ||||||||||||
| Log Level |
Defines the level of detail written to the server log, allowing administrators to control the amount and type of runtime information recorded.
|
||||||||||||
| Backlog | Specifies the maximum number of pending client connection requests allowed in the server’s queue before new requests are refused. Adjusting this value helps balance connection handling under heavy load by controlling how many simultaneous requests can wait for service. | ||||||||||||
| Blocking |
|
||||||||||||
| Keystore | Specifies the keystore for SSL/TLS, identifying the alias that provides certificates when SSL is enabled. Clicking the  icon opens the file browser; selecting the icon opens the file browser; selecting the  icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. |
||||||||||||
| Keystore Password | Password for accessing the specified keystore. | ||||||||||||
| Use SSL |
|
||||||||||||
| Skip rhost Verification |
|
||||||||||||
| Skip Ident Verification |
|
||||||||||||
| Scan All Roots |
|
||||||||||||
| Prefixes | When the list is empty, no prefixes are defined for path mapping. Clicking the  icon opens the Add Prefix dialog, where an administrator enters a new prefix and confirms with OK, resulting in the prefix being added to the list for server use. The icon opens the Add Prefix dialog, where an administrator enters a new prefix and confirms with OK, resulting in the prefix being added to the list for server use. The  icon removes a selected prefix, while the icon removes a selected prefix, while the  and and  icons adjust the order of entries in the list. icons adjust the order of entries in the list. |
||||||||||||
| DSKSYN | Defines drive synonyms that map logical drive identifiers to physical directories. Clicking the  icon opens the Add DSKSYN dialog, and confirming with OK adds the synonym to the list. Selecting a created DSKSYN and clicking the icon opens the Add DSKSYN dialog, and confirming with OK adds the synonym to the list. Selecting a created DSKSYN and clicking the  removes it from the configuration, enabling direct management of drive associations. removes it from the configuration, enabling direct management of drive associations. |
Port Request
The Port Request Server handles client connection requests and directs them to available BBjServices, serving as an entry point for new sessions. Configuration fields specify the bind address that determines which network interface accepts requests, the port number used for communication, and the maximum number of simultaneous clients supported. Enabling the Start option ensures the service actively listens for and manages incoming connections, providing controlled access to the BBj runtime environment.
Port Request Settings List
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Start |
|
| Bind Address | Sets the IP address/interface, the Port Request server binds to for incoming client requests; 127.0.0.1 limits access to the local machine, while 0.0.0.0 accepts connections from any address. |
| Port |
TCP/IP port used by the Port Request Server to listen for client requests; the default is 2008, configurable in Enterprise Manager. |
| Maximum Clients | Limits the number of concurrent client connections the Port Request service can accept. Setting this value prevents overload by restricting access once the defined client threshold is reached. |
PRO/5 DS
The PRO/5 DS server allows remote access to traditional PRO/5 data and logic through the BBjServices framework. It includes two sub-components: PRO/5 DS for data server communication and Memory Mapped Protocol for shared memory-based data access to improve performance on local systems.
PRO/5 DS Settings List
| Settings |
Description |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start |
|
||||||||||||
| Interface | Defines the IP address or network interface on which the server listens for client requests. The default value 0.0.0.0 binds the service to all available network interfaces, allowing connections from any configured address. | ||||||||||||
| Port | Specifies the TCP port used by the PRO/5 Data Server to listen for and accept client requests. Assigning a unique port prevents conflicts with other services and ensures proper client-server communication. | ||||||||||||
| Log File Base | Sets the file path where the server writes its log data. | ||||||||||||
| Log File Size (MB) | Maximum size of the log file before rollover. | ||||||||||||
| Keep Logs (Days) | Determines how many days log files are retained before deletion. | ||||||||||||
| Debug Level | Controls the depth of diagnostic information written to the log for the PRO/5 Data Server. Level 0 produces no debug output, while higher levels (1–4) progressively increase the detail of captured events, aiding in troubleshooting and performance analysis. | ||||||||||||
| Log Level |
Defines the level of detail written to the server log, allowing administrators to control the amount and type of runtime information recorded.
|
||||||||||||
| Backlog | Sets the maximum number of client connections that can wait in the server’s TCP listen queue; once this queue is full, new attempts are refused until space becomes available. | ||||||||||||
| Blocking |
|
||||||||||||
| Keystore | Specifies the keystore for SSL/TLS, identifying the alias that provides certificates when SSL is enabled. Clicking the  icon opens the file browser; selecting the icon opens the file browser; selecting the  icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. |
||||||||||||
| Keystore Password | Provides the password to access the specified keystore. |
PRO/5 DS
The PRO/5 Data Server sub-component manages access to legacy PRO/5 data files, enabling BBjServices to process PRO/5 applications and databases within a modern service environment. Configuration options control startup behavior, SSL encryption, authentication, advisory locking, key handling, timeouts, and file system mapping, allowing administrators to maintain backward compatibility while applying secure and efficient server management practices.
PRO/5 DS Settings List
| Settings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Service | Identifies the active service as the PRO/5 Data Server, which provides connectivity and processing support for legacy PRO/5 data files within BBjServices. |
| Enabled |
|
| Use SSL |
|
| Skip rhost Verification |
|
| Skip Ident Verification |
|
| NTDS Authentication |
|
| NTDS Open Access |
|
| Advisory Locking |
|
| 64-bit MKEYED |
|
| Tagged |
|
| Mask MKEYED FID |
|
| Umask | Defines the default permission mask applied by the PRO/5 Data Server when creating files or directories. The numeric value removes specific permissions from the system defaults (files: 666, directories: 777); for example, setting 022 results in files with permissions 644 and directories with permissions 755. See: Interface ConnectionMgr. |
| Default Timeout | Defines the number of seconds the PRO/5 Data Server waits for a busy record or file before returning an error; valid range is 4–255 seconds, with a default of 10 seconds. See: Configuration Files. |
| Keep Backslashes |
|
| Scan All Roots |
|
| Prefixes | When the list is empty, no prefixes are defined for path mapping. Clicking the  icon opens the Add Prefix dialog, where an administrator enters a new prefix and confirms with OK, resulting in the prefix being added to the list for server use. Clicking The icon opens the Add Prefix dialog, where an administrator enters a new prefix and confirms with OK, resulting in the prefix being added to the list for server use. Clicking The  icon removes a selected prefix, while the icon removes a selected prefix, while the  and and  icons adjust the order of entries in the list. icons adjust the order of entries in the list. |
| DSKSYN | Defines drive synonyms that map logical drive identifiers to physical directories. Clicking the  icon opens the Add DSKSYN dialog, and confirming with OK adds the synonym to the list. Selecting a created DSKSYN and clicking the icon opens the Add DSKSYN dialog, and confirming with OK adds the synonym to the list. Selecting a created DSKSYN and clicking the  removes it from the configuration, enabling direct management of drive associations. removes it from the configuration, enabling direct management of drive associations. |
PRO/5 DS > Memory Mapped Protocol
The Memory Mapped Protocol (MMP) provides a high-performance mechanism for accessing PRO/5 and BBj data files by mapping them directly into system memory. As a sub-component of the PRO/5 Data Server, it reduces disk I/O overhead and accelerates file access while maintaining compatibility with server-managed features such as locking, file permissions, and extended storage formats. Configuration options, including SSL usage, file permissions, locking behavior, and timeout values, allow administrators to balance security, performance, and reliability when enabling memory-mapped access within the Enterprise Manager. See: PRO/5 Memory Mapped Data Server Access.
Memory Mapped Protocol Settings List
| Settings | Descriptions | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enabled |
|
||||||||||
| Use SSL |
|
||||||||||
| MMP File Permissions |
Provides PRO/5 applications with direct file access through the BBj PRO/5 Data Server without going through the TCP/IP layer. It works when both systems run on the same host and connect using 127.0.0.1 , configuration is handled through !DSOPEN or the config.bbx file, and remains transparent to application code. This approach delivers significant performance gains, especially in multi-user, read-heavy environments. Security and performance are managed with the same controls available to other connections, including SSL, file permissions, locking, and timeout settings.
|
||||||||||
| Advisory Locking |
|
||||||||||
| 64-bit MKEYED |
|
||||||||||
| Tagged |
|
||||||||||
| Mask MKEYED FID |
|
||||||||||
| Umask | Defines the default permission mask applied by the PRO/5 Data Server when creating files or directories. The numeric value removes specific permissions from the system defaults (files: 666, directories: 777); for example, setting 022 results in files with permissions 644 and directories with permissions 755. See: Interface ConnectionMgr. | ||||||||||
| Default Timeout | Defines the number of seconds the PRO/5 Data Server waits for a busy record or file before returning an error; valid range is 4–255 seconds, with a default of 10 seconds. See: Configuration Files. | ||||||||||
| Keep Backslashes |
|
||||||||||
| Scan All Roots |
|
||||||||||
| Prefixes | When the list is empty, no prefixes are defined for path mapping. Clicking the  icon opens the Add Prefix dialog, where an administrator enters a new prefix and confirms with OK, resulting in the prefix being added to the list for server use. Clicking The icon opens the Add Prefix dialog, where an administrator enters a new prefix and confirms with OK, resulting in the prefix being added to the list for server use. Clicking The  icon removes a selected prefix, while the icon removes a selected prefix, while the  and and  icons adjust the order of entries in the list. icons adjust the order of entries in the list. |
Proxy Manager
Manages client connection routing between BBj services and external applications, providing a centralized access point for session handling and load distribution. Configuration includes binding to a specific network address, defining the listening port, and limiting the maximum number of concurrent clients. Ensures efficient and secure communication by controlling how client requests are accepted and distributed across the BBj service environment. See: XCALL Client Proxy Server.
Proxy Manager Settings List
|
Settings |
Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Start |
|
| Bind Address | Specifies the network interface the Proxy Manager binds to for listening to client connections. Entering 127.0.0.1 restricts access to local connections only, while using a host IP address or 0.0.0.0 allows external clients to connect. Careful selection is essential for balancing accessibility with security requirements. |
| Port | TCP port number(e.g., 2009) used by the Proxy Manager to accept incoming client connections. Must match the client’s configured proxy port and be open and unused on the host; a wrong, blocked, or conflicting port prevents clients from connecting through the proxy. |
| Maximum Clients | Limits the number of concurrent client connections the Port Request service can accept. Setting this value prevents overload by restricting access once the defined client threshold is reached. |
SQL Engine Server
The SQL Engine Server provides the runtime service that executes BBj SQL operations, handling client connections, queries, and transaction requests through a designated TCP port. Configuration options such as interface binding, logging, debugging, and connection management allow administrators to optimize both performance and security. The server plays a central role in enabling data access, ensuring that applications interact reliably with databases under controlled, monitored conditions.
SQL Engine Server Settings List
| Settings | Descriptions | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start |
|
||||||||||||
| Interface | Defines the IP address or network interface on which the server listens for client requests. The default value 0.0.0.0 binds the service to all available network interfaces, allowing connections from any configured address. | ||||||||||||
| Port | Defines the TCP port used by the SQL Engine Server to listen for client connections. The default setting is 2001, but this value can be changed to match system requirements or avoid conflicts with other services. Configuring the wrong port prevents clients from connecting to the SQL Engine Server, so the value must align with client connection settings. | ||||||||||||
| Log File Base | Specifies the directory and file path (e.g., C:\bbx\log\SQLServer.log) where the server writes its log files for operational tracking. | ||||||||||||
| Log File Size (MB) | Sets the maximum size in megabytes for individual log files before they are rotated or overwritten. | ||||||||||||
| Keep Logs (Days) | Determines how many days log files are retained before being deleted automatically to save storage space. | ||||||||||||
| Debug Level | The diagnostic detail written to the server log: Level 0 records no debug output, while Levels 1–4 progressively increase the depth of diagnostic information up to the most detailed output for troubleshooting (higher levels produce larger logs and can affect performance). | ||||||||||||
| Log Level |
Defines the level of detail written to the server log, allowing administrators to control the amount and type of runtime information recorded.
|
||||||||||||
| Backlog | Sets the maximum number of client connections that can wait in the server’s TCP listen queue; once this queue is full, new attempts are refused until space becomes available. | ||||||||||||
| Blocking |
|
||||||||||||
| Keystore | Specifies the keystore for SSL/TLS, identifying the alias that provides certificates when SSL is enabled. Clicking the  icon opens the file browser; selecting the icon opens the file browser; selecting the  icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. |
||||||||||||
| Keystore Password | Provides the password to access the specified keystore. | ||||||||||||
| Use SSL |
|
||||||||||||
| Scan All Roots |
|
Terminal
The Terminal server manages connections for BBj® and PRO/5® terminal sessions, handling input and output streams between client devices and the server environment. It provides a dedicated channel for terminal-based applications, allowing multiple clients to connect concurrently while respecting configured limits for address binding, port assignment, and maximum client capacity. This setup ensures stable and efficient communication for applications, balancing performance and accessibility through straightforward configuration.
Terminal Settings List
| Settings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Start |
|
| Bind Address | The network interface where the Terminal server listens for client connections. Setting the value to 127.0.0.1 restricts access to the local machine only, while assigning a specific IP address or 0.0.0.0 allows connections from external hosts. Proper configuration ensures secure and controlled client access. |
| Port | Defines the TCP port used by the Terminal Server to accept client connections. The default is 2004. You can change this to any free port allowed by the firewall, but clients must use the same port. If the port is blocked or already in use, connections will fail. See: Current BBj default ports for the various BBj servers. |
| Maximum Clients | Limits the maximum number of client connections the Terminal Server accepts at once. The default is 500. Increasing this value supports more users but raises system load, while decreasing it limits access and can improve stability on systems with fewer resources. |
Thin Client
The Thin Client server provides the communication channel between BBjServices and BBj Thin Client sessions, allowing applications to run remotely while displaying on the user’s workstation. Configuration includes network binding, port selection, client limits, and optional SSL for secure connections. Additional controls manage console access and remote host permissions, giving administrators flexibility to balance performance, security, and accessibility.
Thin Client Settings List
| Settings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Start |
|
| Use SSL | Default setting is false, meaning SSL encryption is disabled for Thin Client connections. Communication occurs without encryption. |
| Bind Address | IP address the Thin Client service binds to for incoming connections; 0.0.0.0 listens on all network interfaces, while using 127.0.0.1 limits access to the local host and entering a specific host IP restricts listening to that interface. |
| Port | TCP port the Thin Client service listens on for client connections; the default is 2003, and it must match the client’s configuration, changing this value requires using an available port permitted by the firewall, as blocked or in-use ports will prevent connections. See: Current BBj default ports for the various BBj servers. |
| Maximum Clients | Limits the maximum number of client connections the server accepts at once. The default is 500. Increasing this value supports more users but raises system load, while decreasing it limits access and can improve stability on systems with fewer resources. |
| Disallow Console |
|
| Allow Rhosts |
|
Thin Client (SSL)
The Thin Client (SSL) server provides secure, encrypted communication between BBjServices and connected Thin Client sessions using SSL/TLS. It ensures that all data, including user credentials and application traffic, is protected against interception during transmission. Configuration options allow administrators to set the listening port, bind address, client limits, and keystore for SSL certificates, ensuring only trusted and encrypted connections are permitted. This service is critical in environments where sensitive business data requires secure remote access without compromising performance or stability. See: How to Configure a Secure Thin Client.
Thin Client (SSL) Settings List
| Settings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
|
|
| Use SSL | Enforces TLS encryption for the Thin Client (SSL) service. With this set to true (as shown), the server accepts only SSL/TLS Thin Client connections using the configured keystore/certificates; clients must connect with SSL-enabled options -SC to succeed. See: Socket Overview. |
| Bind Address | Specifies the IP address the Thin Client (SSL) server binds to for incoming connections 0.0.0.0 listens on all interfaces; 127.0.0.1 restricts access to the local machine; a specific IP limits access to that interface only. Use this to control network exposure and match your security policy. |
| Port | Defines the TCP port the Thin Client (SSL) server listens on for secure client connections; the default is 2103. Clients and firewalls must use the same port or connections will fail. See: Current BBj default ports for the various BBj servers. |
| Maximum Clients | Limits the maximum number of client connections the server accepts at once. The default is 500. Increasing this value supports more users but raises system load, while decreasing it limits access and can improve stability on systems with fewer resources. |
| Disallow Console |
|
| Allow Rhosts |
|
| Keystore | Specifies the keystore for SSL/TLS, identifying the alias that provides certificates when SSL is enabled. Clicking the  icon opens the file browser; selecting the icon opens the file browser; selecting the  icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. |
| Keystore Password | Provides the password needed to access the SSL keystore file where certificates are stored. |
| Client Keystore Password | Specifies the password used to unlock the client’s keystore file during SSL authentication. The value entered here must match the password defined when the keystore was created; otherwise, SSL connections fail. Ensuring the correct password protects the integrity of the client’s SSL certificates and maintains secure communication. See: How to Configure a Secure Thin Client. |
Thin Client Proxy
The Thin Client Proxy acts as an intermediary service that manages and optimizes Thin Client connections to BBj Services. It handles incoming requests on a defined bind address and port, balancing multiple sessions while enforcing the maximum client limit. By separating client traffic from direct server connections, the proxy improves scalability, centralizes session control, and supports more efficient resource allocation. See: XCALL Client Proxy Server.
Thin Client Proxy Settings List
| Settings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Start |
|
| Bind Address | Specifies the network interface the Thin Client Proxy binds to for listening to client connections. The default value 127.0.0.1 restricts access to the local machine only, blocking remote clients. Changing this to 0.0.0.0 or a specific host IP allows external clients to connect, depending on firewall and security policies. |
| Port | Defines the TCP port number the Thin Client Proxy uses to listen for incoming client connections. The default value is 2006. Administrators can reassign this to any available port permitted by the host firewall, but all connecting clients must be configured to use the same port. Using a blocked or occupied port prevents connections from being established. |
| Maximum Clients | Limits the maximum number of client connections the server accepts at once. The default is 500. Increasing this value supports more users but raises system load, while decreasing it limits access and can improve stability on systems with fewer resources. |
Web
The Web server component of BBj Services handles HTTP and HTTPS traffic, providing the foundation for delivering BBj applications through a browser. Configuration options define the listening port, host identity, and security protocols, including SSL for encrypted connections. Administrators can enable or disable HTTP and SSL support as needed and control whether aliases are permitted for flexible URL routing. By fine-tuning these parameters, the Web server ensures secure and efficient access to BBj web applications. See: BBj Web Server.
Web Settings List
| Settings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
|
|
| HTTP Port | Defines the TCP port on which the Web Server listens for standard HTTP requests. The default is 8888. Administrators may change this to any open port permitted by the host firewall. Using a blocked or already-in-use port prevents browser connections to BBj applications. |
| Hostname | Defines the DNS name used by the BBj Web server. Clients must connect using this name, and the request must include it in the Host header unless Allow Aliases is checked. This setting only controls the expected server name; the network interface used for listening is determined separately by the Bind Address option. See: BBj Web Server. |
| Enable HTTP |
|
| Enable SSL |
|
| Allow Aliases |
|
XCALL
The XCALL server enables remote procedure calls between distributed BBj environments, allowing external applications or BBj processes to securely invoke server-side functions. Configuration options include network binding, port assignment, logging levels, backlog handling, and SSL security settings, ensuring controlled connectivity and traceable activity. Default values, such as port 4444 and log retention for seven days, provide a balanced setup, while administrators can adjust parameters like debug levels, SSL usage, and user enforcement for stricter control. XCALL Server.
XCALL Settings List
| Settings | Descriptions | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start |
|
||||||||||||
| Interface | Defines the network interface address the XCALL service listens on for client connections. The default value 0.0.0.0 binds the service to all available network interfaces, allowing connections from any configured address on the host. Specifying a particular IP address restricts access to that interface only, providing more controlled connectivity. | ||||||||||||
| Port | The TCP port number used by the XCALL server to accept client connections. The default is 4444. Administrators may change this value to any unused port permitted by the host firewall, but connected clients must be configured with the same port. Selecting a port already in use or blocked by the system will prevent successful connections. | ||||||||||||
| Log File Base | The full path and filename prefix where the XCALL server log files are written. The defined base path determines both the directory location and the root name used when generating log files. Proper configuration ensures logs are stored in an accessible directory with adequate disk space for monitoring and troubleshooting server activity. | ||||||||||||
| Log File Size (MB) | Defines the maximum size, in megabytes, that each XCALL service log file can reach before rollover occurs. Once the specified limit is met, a new log file is created to prevent uncontrolled growth and preserve disk space. The default value is 10 MB, providing a balance between detailed logging and efficient storage management. | ||||||||||||
| Keep Logs (Days) | Determines how many days log files are retained before being deleted automatically to save storage space. | ||||||||||||
| Debug Level | The level of diagnostic detail written to the log for the XCALL server. Level 0 produces minimal output, intended for normal operation. Higher levels (1 through 4) progressively increase the amount of detail, with Level 4 generating the most verbose information, typically used for troubleshooting and in-depth analysis. The default is Level 0 to minimize overhead while still capturing essential information. | ||||||||||||
| Log Level |
Defines the level of detail written to the server log, allowing administrators to control the amount and type of runtime information recorded.
|
||||||||||||
| Backlog | Defines the maximum number of pending client connection requests allowed in the queue before the server rejects new ones. A value of 0 uses the host system’s default backlog setting. Higher values let more clients wait during peak load, while lower values reduce wait time but increase the likelihood of refused connections. | ||||||||||||
| Blocking |
|
||||||||||||
| Keystore | Specifies the keystore for SSL/TLS, identifying the alias that provides certificates when SSL is enabled. Clicking the  icon opens the file browser; selecting the icon opens the file browser; selecting the  icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. icon launches the Create New Folder dialog to define a directory, and after confirming with OK, the administrator returns to the browser to locate and select the keystore file, finalizing the choice with Open. |
||||||||||||
| Keystore Password | Provides the password needed to access the SSL keystore file where certificates are stored. See: KB – How to Configure a Secure Thin Client | ||||||||||||
| Use SSL |
|
||||||||||||
| Skip rhost Verification |
|
||||||||||||
| Default User | The BBjServices account automatically assigned to client connections when no credentials are provided. Leaving this field blank requires each client to authenticate explicitly with a valid username. Defining a default user streamlines access but reduces accountability and should only be applied in trusted environments where simplified authentication is appropriate. | ||||||||||||
| Force Default User |
|
||||||||||||
| Default Config | The configuration file automatically applied to XCALL sessions when no client-specific configuration is provided. The specified file sets runtime parameters such as environment variables, paths, and behavior defaults. Proper use ensures consistent startup conditions for all sessions, while administrators can override settings through explicit configurations if required. | ||||||||||||
| Force Default Config |
|
||||||||||||
| Default Working Dir | The startup directory path used when a client session begins. The specified location determines where programs execute relative to the file system and where files are read or created by default. Setting a clear working directory ensures consistent runtime behavior and prevents errors from missing or misdirected file references. | ||||||||||||
| Force Default Working Dir |
|

