 EM: Web > Context Configuration
EM: Web > Context Configuration
Description
In BBj 17.0 and higher, the  Context Configuration page allows administrators to manage multiple web application contexts through the integrated Jetty web server. Each context defines a web application deployment path and settings, and resolves to a unique URL endpoint. The configuration supports embedded DWC apps, BUI apps, SOAP services, BBxServlets and additional content served via Jetty. Furthermore it includes several predefined contexts (root, Enterprise Manager, htdocs, and GoldMine, with minimal configuration, enabling quick deployment of web services. The root context acts as the default host for HTML content and applications such as DWC and BUI.
Context Configuration page allows administrators to manage multiple web application contexts through the integrated Jetty web server. Each context defines a web application deployment path and settings, and resolves to a unique URL endpoint. The configuration supports embedded DWC apps, BUI apps, SOAP services, BBxServlets and additional content served via Jetty. Furthermore it includes several predefined contexts (root, Enterprise Manager, htdocs, and GoldMine, with minimal configuration, enabling quick deployment of web services. The root context acts as the default host for HTML content and applications such as DWC and BUI.
Location
![]() EM Navigator →
EM Navigator →  Web →
Web →  Context Configuration
Context Configuration
Toolbar
| Button | Function |
|---|---|

|
Stops the selected web context and disables access to its deployed applications. |

|
Starts the selected web context and enables access to its deployed applications. |

|
Restarts the selected web context, reloading its configuration and deployed applications. |

|
Launches the selected web context in the system’s default browser. |

|
Adds a new entry and opens new application. |

|
Removes/deletes selected application(s) or files from the system. |

|
Edits selected application(s) / files. |

|
Enables to choose a folder/file from your local system. |
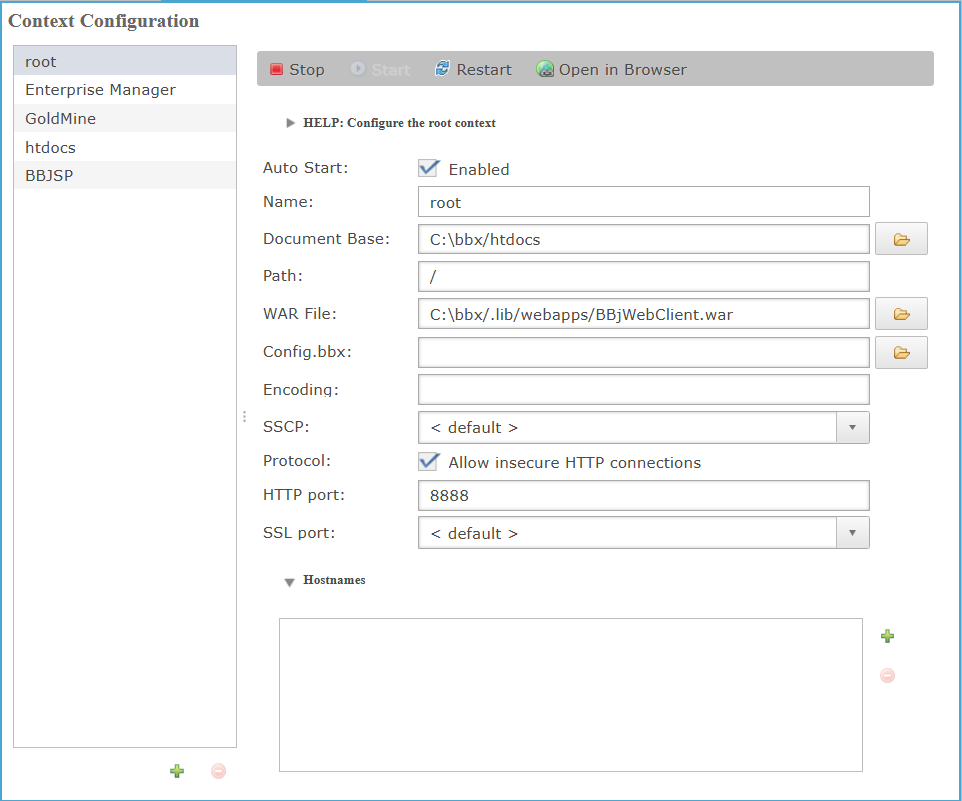
Contexts List
The Contexts List on the left side of the window displays a list of all active contexts, including root, Enterprise Manager, GoldMine, BBJSP, and htdocs. Each context can be individually selected to modify settings related to deployment, security, file paths, and runtime behavior. All contexts share the same configuration framework as root, allowing consistent control and management of their environment.
Context Configuration
Click a context from Context List to display the Context Configuration panel on the right. It allows administrators to view and manage deployment settings for all configured web contexts in the BBj Jetty web server. These settings include the document base directory, WAR file location, HTTP/SSL ports, and session cookie options. Each context such as root, Enterprise Manager, GoldMine, and htdocs individually configured based on application needs.
Context Configuration Properties
Hostnames
Displays hostnames assigned to the current web context. Clicking the  opens a dialog to add a new hostname.
opens a dialog to add a new hostname.
Welcome Files
The list of welcome files for this web context that are automatically served when a client accesses a directory without specifying a file. Clicking the  opens a dialog to define an additional welcome file entry. This enables explicit control over the default file presented at the application’s base URL.
opens a dialog to define an additional welcome file entry. This enables explicit control over the default file presented at the application’s base URL.
BBx Servlets
The BBxServlets panel lists all configured servlets associated with the current web context, detailing each servlet’s URL mapping source, .bbx file path, and implementing Java class. Clicking the  launches the BBxServlet Configuration dialog, where users can define or modify servlet behavior by enabling the servlet, specifying its URL mapping, class name, method, configuration file, SSCP context, terminal alias, and working directory etc. The dialog also allows adding key-value parameter pairs for runtime customization. See: BBXServlet Tutorial.
launches the BBxServlet Configuration dialog, where users can define or modify servlet behavior by enabling the servlet, specifying its URL mapping, class name, method, configuration file, SSCP context, terminal alias, and working directory etc. The dialog also allows adding key-value parameter pairs for runtime customization. See: BBXServlet Tutorial.
BBx Servlet Configuration Properties
| Setting | Description | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enabled |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| URL Mapping | The servlet's URL mapping used to route incoming HTTP requests to the corresponding BBxServlet. It defines the endpoint path that clients access, ensuring the servlet is invoked when that path is requested. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Source File | The full path to the BBx source file used in servlet execution. Clicking the  opens a file browser for selecting an existing .bbx file that defines the servlet logic triggered by the configured URL mapping. opens a file browser for selecting an existing .bbx file that defines the servlet logic triggered by the configured URL mapping. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Class Name | The name of the BBj class to be instantiated when the servlet is invoked. This class must be defined in the associated .bbx source file and implement the servlet’s runtime logic. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method Name | Displays the name of the BBxServlet method invoked at runtime, which processes incoming HTTP requests. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Config File | The path to the configuration file used to initialize BBxServlet runtime properties. Clicking  opens a file browser for selecting a .properties file, by clicking opens a file browser for selecting a .properties file, by clicking  you can create a new server directory. A valid BBj properties file is required for proper servlet initialization. you can create a new server directory. A valid BBj properties file is required for proper servlet initialization. |
||||||||||||||||||
| SSCP |
The SSCP configuration to associate with BBjServices security context. Selecting an entry defines how the web application communicates with secure BBjServices session. See: Session Specific Classpath(SSCP).
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Terminal Alias | The alias BBj uses when opening a terminal session (e.g., in Thin Client or SysConsole environments). This alias corresponds to the SETTERM or alias entry in your config.bbx file and determines the device name (e.g., T0, X0, etc.) used by the servlet. See: BBXServlet Tutorial. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Working Directory | The absolute path to the working directory that the BBxServlet will use during execution. Clicking the  opens a folder browser to select an existing server directory, by clicking opens a folder browser to select an existing server directory, by clicking  allows users to create a new subdirectory. allows users to create a new subdirectory. |
Parameters
The Parameters define user-defined Name-Value pair that serve as initialization parameters for the servlet during runtime. These entries enable customization of the servlet’s behavior or allow required configuration values to be passed dynamically.
Parameters Properties
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The key of the name-value pairs used to pass initialization parameters to the servlet. This key must match what the servlet retrieves using BBjServletConfig.getParameter(name) to ensure proper configuration at runtime. |
| Value |
The data assigned to the corresponding parameter key, passed to the servlet as an initialization value. This value is retrieved in servlet logic using BBjServletConfig.getParameter it is used to control runtime behavior and pass configuration settings dynamically. |
BBJSP Servlets - Deprecated
Note: This panel is deprecated and no longer recommended for use in current projects. Users are advised to transition to the BBxServlet framework introduced in BBj 18.00, which offers enhanced functionality, modern standards compliance, and full integration with BBj’s session-managed servlet infrastructure.
BBj Servlets - Deprecated
Note: This panel is deprecated and no longer recommended for use in current projects. Users are advised to transition to the BBxServlet framework introduced in BBj 18.00, which offers enhanced functionality, modern standards compliance, and full integration with BBj’s session-managed servlet infrastructure.
Java Servlets
Displays a configuration panel to register and manage standard Java servlets within the selected web context. Click the  to open the Servlet Configuration dialog, where you define the URL mapping, Java class name, and optional initialization parameters. This enables custom Java-based request handling directly through the BBj Jetty web server.
to open the Servlet Configuration dialog, where you define the URL mapping, Java class name, and optional initialization parameters. This enables custom Java-based request handling directly through the BBj Jetty web server.
Java Servlet Configuration Properties
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Mapping | The URL pattern used to invoke the servlet within this web context. This mapping configures how incoming requests are routed to the servlet's handler method. |
| Class Name | Java class name that implements the servlet logic. This must match the class in the servlet source and be loadable through the selected SSCP to run correctly. |
Parameters
The Parameters define user-defined Name-Value pair that serve as initialization parameters for the servlet during runtime. These entries enable customization of the servlet’s behavior or allow required configuration values to be passed dynamically.
Parameters Properties
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The key of the name-value pairs used to pass initialization parameters to the servlet. This key must match what the servlet retrieves using BBjServletConfig.getParameter(name) to ensure proper configuration at runtime. |
| Value |
The data assigned to the corresponding parameter key, passed to the servlet as an initialization value. This value is retrieved in servlet logic using BBjServletConfig.getParameter it is used to control runtime behavior and pass configuration settings. |
Enable BBJSP
Note: When unchecked, the BBJSP Configuration, BBJSP Pipelines, BBJSP Commands, Database Driver, and Database Table sections are hidden and BBJSP functionality is disabled for this context. When checked, all those sections become visible and configurable, enabling BBJSP pages, commands, database connectivity, and pipeline setup within the web context.
BBJSP Configuration
Configures core settings for the BBJSP framework in the selected web context. Users can configure the BBj runtime user, enable development mode, update tag libraries, set file extensions for pages and commands, and specify the command log path. The panel also supports servlet configuration, database connection details, and session table definitions for BBJSP session management.
BBJSP Configuration Properties
| Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
| BBj User | The BBj runtime user under BBJSP pages and commands execute in this web context. This determines the permissions and server identity used during request processing. |
| Development Mode |
|
| Update BBJSP Tag Libraries | The button to update BBJSP tag libraries for the selected web context.
When clicked, It copies the necessary BBJSP tag library files from the BBj JAR into the context’s document base, typically the WEB-CFG/tld directory. This step is required for the server to recognize and interpret BBJSP tags embedded in HTML pages. Without this update, BBJSP functionality will not work.
Note: Although BBJSP is deprecated, updating tag libraries is still essential for legacy support.
|
| Page Extension | The file extension used to identify BBJSP pages within this web context (e.g., bbjsp). This extension determines which URLs are processed by the BBJSP engine, enabling the system to correctly route BBJSP content. |
| Command Extension | BBj user, which defines the BBj runtime account under BBJSP pages and commands execute. This ensures the correct user permission is applied to all BBJSP operations. |
| Command LogFile | The file path used to store BBJSP command execution logs. Clicking the  opens a file browser to select a different existing log file on the server. This log captures BBJSP command activity and is essential for troubleshooting within Enterprise Manager. opens a file browser to select a different existing log file on the server. This log captures BBJSP command activity and is essential for troubleshooting within Enterprise Manager. |
BBJSP Pipelines
Configures pipeline work-flows for the selected web context using XML files. Each pipeline runs sequential BBj stages with optional branching to manage complex logic. Triggered via BBJSP pages or commands, pipelines use BBjspSessionData for session handling. Clicking the  opens a dialog to name the pipeline, select config files, and assign BBj sources and Java classes to each stage.
opens a dialog to name the pipeline, select config files, and assign BBj sources and Java classes to each stage.
Pipeline Configuration Properties
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The unique identifier assigned to the BBJSP pipeline definition within the current web context. This name is used internally to reference and invoke the configured pipeline when processing BBJSP page or command requests. |
| BBj Config File | The BBj configuration file path used to initialize pipeline settings. Clicking  the opens a file browser to select a .properties file. the opens a file browser to select a .properties file. |
| Pipeline Config File | The XML file path that defines BBJSP pipeline stages and execution flow. Clicking the  opens your local director to choose a configuration file. opens your local director to choose a configuration file. |
Stages Properties
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name assigned to an individual stage within a BBJSP pipeline, serving as its identifier in both the configuration list and runtime logs. |
| Source | The source identifier for the pipeline stage, referencing the BBj program or handler defined in the pipeline configuration file. |
| Class | The fully qualified Java class name that implements the servlet’s request handling logic. This must match the class defined in your source file and be accessible via the selected SSCP at runtime to ensure proper servlet execution. |
BBJSP Commands
Defines BBJSP commands within the selected web context by mapping a URL path to a BBx source file and Java class, enabling execution of back-end logic through HTTP requests. Each command can specify an input BBJSP page, trigger an associated pipeline, and configure post-execution redirects. Clicking the  opens Command Configuration dialog to enter path, file, class, input page, pipeline. Redirects settings enabling separation logic, processing, and navigation within BBJSP applications.
opens Command Configuration dialog to enter path, file, class, input page, pipeline. Redirects settings enabling separation logic, processing, and navigation within BBJSP applications.
BBJSP Commands Properties
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The URL path segment that triggers this BBJSP command. This path must match the route specified in your web.xml or EM configuration so HTTP requests invoke the correct BBx program. |
| Source File | The file path to the BBx source program that defines the back-end logic for the command. Clicking the  opens the file browser to locate and select the source file used for execution. opens the file browser to locate and select the source file used for execution. |
| Class Name | The fully qualified Java class name that handles BBJSP command execution, enabling EM to dynamically instantiate and invoke the appropriate handler method during HTTP request processing. |
| Input Page | The path to the BBJSP input page that opens before the command runs, providing the user-facing interface where users interact before back-end processing begins. |
| Pipeline | The name of the BBJSP pipeline to invoke after the command executes, enabling multistage logic processing through a defined sequence of BBj programs configured in the selected web context. |
Redirects
The list of post-command routing rules, where each entry maps a command result to a destination path and optionally triggers a pipeline. The Redirect column controls whether the client browser is redirected (true) or internal forwarding is used (false), enabling flexible response handling after BBJSP command execution.
Redirects Properties
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name assigned to a redirect entry, used to distinguish redirect behaviors for specific BBJSP command outcomes within the routing configuration. |
| Path | The relative URL path used to match the command result and trigger the associated redirect rule within the BBJSP command configuration. |
| Pipeline | The name of the BBJSP pipeline to invoke after the command executes, enabling multistage logic processing through a defined sequence of BBj programs configured in the selected web context. |
| Redirect | The specified redirect path is triggered after the BBJSP command executes, allowing conditional navigation to another URL based on a true (redirect) or false (no redirect) value. |
Context LogFile & Size MB Properties
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Context LogFile | The absolute file path to the BBJSP engine log used by the current web context for runtime details. Clicking the  opens a file selector to specify or change the target log file. opens a file selector to specify or change the target log file. |
| Size MB | The maximum file size limit (in megabytes) for the BBJSP context log before it triggers log overwriting. This setting helps manage disk usage by controlling how large the log file can grow. |
Database Driver
Configures the connection settings required to link the BBJSP context to a BBj managed database, including the JDBC driver class, connection URL, database, and authentication credentials. This configuration enables BBJSP components to perform data operations using the specified database backend.
Database Driver Properties
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Driver Class | The JDBC driver class used to connect BBJSP applications to the BBj SQL engine, such as com.basis.jdbc.BasisDriver, enabling SQL communication via the BBj JDBC interface. |
| URL | The JDBC connection URL used by the BBJSP engine to locate and connect to the BBj SQL database server, typically including the protocol, host, and port (e.g., jdbc:basis:localhost:2001). |
| Database | The name of the BBj database to which the BBJSP engine connects, enabling SQL operations within the application context. |
| Database User | The username used to authenticate the JDBC connection to the specified BBj database, enabling authorized access for BBJSP-driven SQL operations. |
| Password | The password used to authenticate the database user for establishing a connection to the specified BBj SQL database through the configured JDBC driver. |
Database Table
Configures settings for the database table that manages BBJSP pipeline session data, enabling stateful session tracking by storing and retrieving session context through the BBj SQL database.
Database Table Properties
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Table Name | The name of the database table used to store BBJSP pipeline session data, enabling persistence of session state across multiple pipeline executions. |
| ID column | The name of the database column used to uniquely identify each BBJSP pipeline session record, ensuring session data can be accurately stored and retrieved during pipeline execution. |
| DATA column | The name of the database column used to store serialized BBJSP pipeline session data, preserving session-specific state information between requests. |
| TIMESTAMP column | The name of the database column used to record the last time the BBJSP pipeline session data was updated, enabling time-based session tracking and cleanup. |
Start-Stop Programs
Displays the configuration paths for optional BBJSP programs that automatically run at key life-cycle, when a web context or user session starts or stops. Clicking  next to each field opens a file browser dialog to select the corresponding program file. These entries allow administrators to define initialization or cleanup routines tied to BBJSP session.
next to each field opens a file browser dialog to select the corresponding program file. These entries allow administrators to define initialization or cleanup routines tied to BBJSP session.
Start-Stop Programs Properties
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Context Start Program | The file path to a BBJSP program that runs automatically at web context startup. Clicking the  opens file browser to select the program used for initialization. opens file browser to select the program used for initialization. |
| Context Stop Program | The file path to a BBJSP program that runs automatically during web context shutdown. Clicking the  opens a file browser to select a cleanup or termination. opens a file browser to select a cleanup or termination. |
| Session Start Program | The file path to a BBJSP program that runs automatically when a user session starts. Clicking the  opens a file browser dialog to select the initialization file for session setup. opens a file browser dialog to select the initialization file for session setup. |
| Session Stop Program | The file path to a BBJSP program that runs automatically when a user session ends. Clicking the  opens a file browser dialog to select the shutdown file, allowing administrators to define cleanup or finalization logic tied to session termination. opens a file browser dialog to select the shutdown file, allowing administrators to define cleanup or finalization logic tied to session termination. |
Override Mappings
Configure fields for overriding default URL path mappings used by BBJSP to route requests for various application types. These include BUI applications, DWC applications, BBJ servlets, and SOAP web services. Customizing these mappings allows administrators to redirect or remap specific URI segments to different handler types and enabling flexible deployment structures.
Override Mappings Properties
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| BUI Applications | The override path segment used to route BUI application requests within the BBJSP context, allowing administrators to customize the URL prefix for accessing deployed applications. |
| DWC Applications | The override path segment used to route DWC (Dynamic Web Client) application requests within the BBJSP context, enabling administrators to customize the default URL prefix for accessing DWC applications. |
| BBJ Servlets | The override path segment used to route BBJ servlet requests within the BBJSP context, allowing customization of the default servlet URL prefix for accessing deployed BBJ servlets. |
| SOAP Web Services | The override path segment for routing SOAP web service requests within the BBJSP context, allowing administrators to customize the default webservice URL prefix used to access deployed SOAP endpoints. |
HTTP Error Pages
Displays a configurable list of HTTP status codes and their corresponding error page URIs to define which custom error page is sent to the client when specific HTTP errors occur within the BBJSP context.
HTTP Error Pages Properties
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| HTTP Error Code | The numeric HTTP status code that triggers a custom error page response within the BBJSP context, enabling precise error handling for specific client or server conditions. |
| HTTP Error URI | The URI path to the custom error page returned when the corresponding HTTP status code is triggered, enabling targeted error page routing within the BBJSP context. |
Default Error Page: Displays the URI path to the default error page returned when no specific HTTP error mapping is defined, ensuring fallback handling for unanticipated client errors.
Initialization Parameters
The list of name-value pairs used to define initialization parameters that are globally accessible to all programs operating within the BBJSP context, allowing consistent configuration across the application life-cycle.
Initialization Parameters Properties
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of a custom initialization parameter available to all programs within the current BBJSP context. |
| Value | The assigned value for the corresponding initialization parameter, which is made accessible to all programs running within the web context. |
Custom HTPP Headers
The name-value pairs for custom HTTP headers added to every response in the current context. These headers let administrators include additional information like security rules, caching settings, or custom tags in each HTTP response.
Custom HTPP Headers Properties
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The header name for a custom HTTP header that will be included in all responses generated within the context. |
| Value | The header value associated with the custom HTTP header name defined for the current context’s HTTP responses. |
Session Cookie
The session cookie settings for controlling cross-site behavior (SameSite), client-side access (HttpOnly), partitioning (Partitioned), and secure transport (Secure). These options allow administrators to enhance privacy, security, and compatibility across browsers.
Session Cookie Properties
| Setting | Description | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SameSite |
The attributes used to control whether the session cookie is sent with cross-site requests. Enabling administrators to fine-tune cookie behavior for security and compatibility.
|
||||||||||
| HttpOnly |
|
||||||||||
| Partitioned |
|
||||||||||
| Secure |
|
Note: the configuration process for contexts such as Enterprise Manager, GoldMine, and htdocs follows the same structure as the root context. All user interface elements and property panels presented in the root context are shared across these contexts as well.