 EM: Security > Settings
EM: Security > Settings
Description
In BBj 19.20 and higher,  Settings page allows administrators to configure authentication methods and password requirements for BBjServices. Under Authentication Types, you can enable or disable supported methods such as BBj Authentication, LDAP/Active Directory, SAML (EM Only), and Windows authentication by checking the corresponding boxes. The Authorization Token Default Expiration field defines the duration (in minutes) that a user's session token remains valid. Password policy settings are managed using the Password Minimum Length and Password Validation Type fields to enforce secure login credentials. These settings help centralize security control and ensure compliance with authentication policies. All changes made here directly affect how users are authenticated when accessing the Enterprise Manager and its associated services.
Settings page allows administrators to configure authentication methods and password requirements for BBjServices. Under Authentication Types, you can enable or disable supported methods such as BBj Authentication, LDAP/Active Directory, SAML (EM Only), and Windows authentication by checking the corresponding boxes. The Authorization Token Default Expiration field defines the duration (in minutes) that a user's session token remains valid. Password policy settings are managed using the Password Minimum Length and Password Validation Type fields to enforce secure login credentials. These settings help centralize security control and ensure compliance with authentication policies. All changes made here directly affect how users are authenticated when accessing the Enterprise Manager and its associated services.
Location
![]() EM Navigator →
EM Navigator →  Security →
Security →  Settings
Settings
Toolbar
Security settings Properties
| Settings | Description | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Authorization Token Default Expiration (minutes) | Defines the number of minutes a user's authentication token remains valid before it expires and re-authentication is required. | ||||||||||
| Authentication Types |
Defines the available authentication methods that BBjServices can use to verify user credentials for accessing Enterprise Manager, ODBC/JDBC connections, and BBj-based authentication, depending on system configuration and platform. Clicking on the entries in this list opens configuration settings specific to that entry.
|
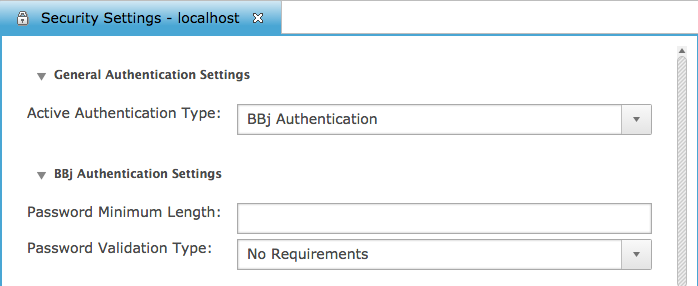
BBj Authentication Settings
To open the BBj Authentication Settings configuration panel, click the BBj Authentication entry under Authentication Types.
LDAP/Active Directory Authentication Settings
To open the LDAP/Active Directory configuration panel, click the LDAP/Active Directory entry under Authentication Types. The LDAP/Active Directory Authentication Settings section lets administrators configure directory server details for user authentication. The panel includes fields for host, port, timeout, bind DN, and search queries to enable centralized user validation. A Secondary Settings panel provides failover support, allowing authentication through a backup server if the primary fails. This setup improves reliability and integrates BBjServices with enterprise directory systems.
Active Directory Authentication Settings Properties
Note: To read more, see: Using LDAP and Active Directory User Authentication in BBj 15.00
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| LDAP/Active Directory Uses SSL |
|
| LDAP/Active Directory Server Host |
Defines the hostname or IP address of the LDAP/Active Directory server that BBjServices will query for user authentication and directory operations. This value must match the network-accessible domain controller used in your organization's identity infrastructure. |
| LDAP/Active Directory Server Port |
Defines the network port used by BBjServices to communicate with the LDAP/Active Directory server, typically port 389 for standard connections or 636 for secure SSL connections. |
| LDAP/Active Directory Server Timeout |
Defines the maximum time in milliseconds that BBjServices will wait for a response from the LDAP/Active Directory server before the connection attempt is terminated. |
| User Match Patterns | Defines one or more LDAP distinguished name (DN) patterns used to locate user accounts during authentication (e.g., uid=%u,dc=example,dc=com). Press the  button to add a new pattern entry, and press the button to add a new pattern entry, and press the  button to delete an existing one. button to delete an existing one. |
| Directory Access Bind DN | Defines the distinguished name (DN) of the user account that BBjServices uses to bind to the LDAP or Active Directory server when performing searches or authentication operations. This account must have read access to the directory structure where user and permission information is stored. |
| Directory Access Password |
Defines password used by the specified bind DN to authenticate against the LDAP/Active Directory server when retrieving user and permission data. |
| Add Permissions LDIF Lines | Defines the LDIF (LDAP Data Interchange Format) entries used to add user permission records to the directory during authentication or configuration. Select the  button to add a new LDIF line, and press the button to add a new LDIF line, and press the  button to delete an existing one. button to delete an existing one. |
| Modify Permissions LDIF Lines | Defines the lines that build the necessary LDIF format entries used to modify user permissions in the directory during updates. Select the  button to add a new LDIF line, and press the button to add a new LDIF line, and press the  button to delete an existing one. button to delete an existing one. |
| User Search Query |
Defines the search query that BBj will use to locate valid users in the LDAP/Active Directory system. Select the |
| Permissions Search Query |
Defines the search query that BBj will use to check user permissions for accessing the Enterprise Manager. Select the |
SAML (EM Only) Settings
To open the SAML authentication configuration panel for Enterprise Manager, click the SAML (EM Only) entry under Authentication Types. This reveals multiple sections: Organization Settings, Service Provider Settings, Identity Provider Settings, and Security Settings. These panels allow you to define how EM integrates with external identity providers via SAML 2.0. You can configure SAML endpoints, x509 certificates, request/response bindings, and signature algorithms to meet your organization's single sign-on (SSO) requirements. All settings must align with your identity provider’s specifications to ensure secure and successful authentication. This integration enables centralized user access management and enhances EM login security.
SAML (EM Only): Organization Settings
The Organization Settings allows administrators to define company-specific metadata displayed during SAML transactions, such as organization name, support contact details, and technical information. These values are used in SAML metadata exchange and help identify the service provider (Enterprise Manager) to identity providers and end users. Accurate input ensures proper branding, traceability, and support channel visibility during authentication work-flow.
Organization Settings Properties
| Settings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Organization Name | Defines the full legal name of the organization that operates the BBj Enterprise Manager. This value appears in SAML metadata and identifies the service provider during authentication exchanges. |
| Organization Display Name | Defines the name of the organization as it will appear in BBj Enterprise Manager UI and SAML identity transactions. This value is typically used for user-facing interfaces and metadata display. |
| Organization Web Site | Defines the organization's official website URL, which is included in SAML metadata and referenced in Enterprise Manager-generated identity provider communications. |
| Organization Language | Defines the primary language code (e.g., en, de, fr) used for organization-related metadata and applied to localized SAML attributes and Enterprise Manager UI language settings. |
| Technical Name | Defines the name of the designated technical contact responsible for Enterprise Manager configuration and SAML identity provider integration support. |
| Technical Email | Defines the email address of the technical contact who receives system notifications and supports Enterprise Manager configuration or SAML integration issues. |
| Support Name | Defines the name of the support contact responsible for assisting users with Enterprise Manager issues, system access problems, and general support inquiries. |
| Support email | Defines the email address for contacting support personnel who assist with Enterprise Manager access issues, operational problems, or system-related support requests. |
SAML (EM Only): Service Provider Settings
The Service Provider Settings allows administrators to configure key SAML metadata parameters that define Enterprise Manager’s identity as a service provider during SAML authentication exchanges. These values include entity identifiers, assertion and logout endpoints, bindings, and cryptographic credentials (certificates and private keys). Accurate configuration ensures secure, trusted communication with identity providers, proper assertion handling, and reliable single sign-on (SSO) and logout workflows within BBj Enterprise Manager environments.
Service Provider Settings Properties
| Settings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| SP Entity ID (BBJ) | Defines the unique service provider entity identifier (Entity ID) used by BBj Enterprise Manager in SAML metadata exchanges, allowing identity providers to recognize and communicate securely with the BBj Enterprise Manager instance. |
| SP Assertion Consumer Service | Defines the service provider endpoint URL where BBj Enterprise Manager receives and processes SAML authentication assertions from the identity provider during single sign-on (SSO) operations. |
| SP Assertion Consumer Service Binding | Defines the SAML binding protocol (e.g., HTTP-POST) that determines how the identity provider transmits authentication assertions to the BBj Enterprise Manager's Assertion Consumer Service endpoint. |
| SP Single Logout Service URL | Defines the service provider endpoint where the identity provider sends SAML logout requests and responses to terminate BBj Enterprise Manager user sessions during Single Logout (SLO) operations. |
| SP Single Logout Service Binding | Defines the SAML protocol binding (e.g., HTTP-Redirect) that determines how logout messages are transmitted between the identity provider and BBj Enterprise Manager during Single Logout (SLO) operations. |
| SP x509 Certificate | Defines the Base64-encoded X.509 certificate used by BBj Enterprise Manager to digitally sign SAML authentication requests and assertions, ensuring message integrity and trust with identity providers during secure SAML transactions. |
| SP Private Key | Stores the PEM-encoded private key used by BBj Enterprise Manager to sign SAML messages, paired with the SP x509 Certificate, ensuring message authenticity and secure trust relationships with identity providers. |
SAML (EM Only): Identity Provider Settings
The Identity Provider Settings section allows administrators to configure essential SAML metadata that identifies and connects BBj Enterprise Manager to the external Identity Provider (IdP). These settings define IdP endpoints for single sign-on (SSO) and single logout (SLO), protocol bindings, cryptographic certificates, and role attribute mappings, ensuring secure authentication, proper role assignment, and trusted communication between Enterprise Manager and the IdP during SAML exchanges.
Identity Provider Settings Properties
| Settings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| IDP Entity Provider URI | Defines the unique identifier (entity ID URI) of the Identity Provider that BBj Enterprise Manager uses to establish trust and exchange SAML metadata for authentication. |
| IDP SSO Endpoint | Defines the Identity Provider's Single Sign-On (SSO) URL where BBj Enterprise Manager sends authentication requests to initiate the SAML login process. |
| IDP Response Protocol Binding | Defines the SAML binding method (e.g., HTTP-Redirect) used by the Identity Provider to deliver authentication responses back to BBj Enterprise Manager. |
| IDP SLO Endpoint | Defines the Identity Provider’s Single Logout (SLO) endpoint URL where BBj Enterprise Manager sends logout requests to terminate user sessions across integrated applications. |
| IDP SLO Response Endpoint | Defines the Identity Provider’s endpoint URL where BBj Enterprise Manager receives responses after initiating Single Logout (SLO) operations, ensuring proper synchronization of user session terminations across integrated authentication systems. |
| IDP SLO Protocol Binding | Defines the SAML protocol binding method (e.g., HTTP-Redirect) that BBj Enterprise Manager uses to communicate Single Logout (SLO) requests and responses with the Identity Provider, ensuring proper message transmission format and compliance with SAML standards. |
| IDP Public_x509 Certificate | Defines the Identity Provider's public x509 certificate used by BBj Enterprise Manager to verify digital signatures on SAML assertions and protocol messages, ensuring secure and trusted authentication communication. |
| IDP Certificate Fingerprint | Defines the cryptographic fingerprint (hash) of the Identity Provider’s x509 certificate used by BBj Enterprise Manager to validate the authenticity of SAML responses and ensure secure certificate matching during authentication exchanges. |
| IDP Certificate Fingerprint Algorithm | Defines the cryptographic hash algorithm (e.g., SHA-1, SHA-256) that BBj Enterprise Manager uses to compute and validate the Identity Provider’s certificate fingerprint for secure SAML message verification. |
| Assertion Role/Group Attribute | Defines the SAML attribute that provides user role or group information to BBj Enterprise Manager during authentication, enabling assignment of permissions based on identity provider assertions. |
| Default Role/Group | Defines the default role or group assigned to users during BBj Enterprise Manager authentication if no role information is provided in the SAML assertion. |
SAML (EM only): Security Settings
The Security Settings allows administrators to configure critical SAML security parameters for BBj Enterprise Manager. These options control signing and encryption of authentication requests, log-out requests, and assertions, define authentication context comparison, specify credential protection mechanisms, and set the signature algorithm used for secure SAML message exchanges. Proper configuration ensures trusted, standards-compliant communication with Identity Providers and safeguards authentication integrity within BASIS Cloud and Enterprise Manager deployments.
Security Settings Properties
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Name ID Encrypted |
|
| Authn Request _Signed |
|
| Logout Request Messages Signed |
|
| Logout Response Messages Signed |
|
| Want Messages Signed |
|
| Want Assertions Signed |
|
| Want Assertions Encrypted |
|
| Want NameID Encrypted |
|
| urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:Password |
Defines the requested authentication context class reference for SAML authentication, indicating that password-based authentication is required when BBj Enterprise Manager interacts with the Identity Provider. |
| Authn Context Comparison | Defines how BBj Enterprise Manager evaluates authentication context class references during SAML login. When set to exact, the Identity Provider must match the requested authentication method to proceed with authentication. |
| Signature Algorithm | Defines the cryptographic algorithm used to sign SAML messages exchanged by BBj Enterprise Manager. The selected URI determines the hash and signing method (e.g., RSA-SHA1, RSA-SHA256), which must match the Identity Provider's supported algorithms to ensure message integrity and trust during SAML transactions. |
